For decades, relational databases have provided the backbone for business applications and financial transactions (OLTP) and data warehouses (OLAP) managing relational structured data stored in rows and columns. I am sure it does not surprise anyone that Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server and SAP HANA are core to these systems and will be for a while. In reality, databases are used just about everywhere including banks, retail, websites and warehouses – to name just a few.
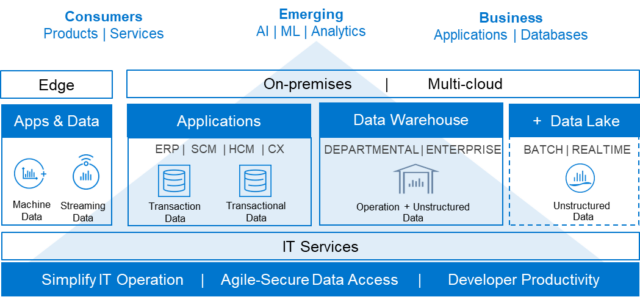
Today, with the proliferation of unstructured, machine and big data, IT is deploying and managing a variety of general and purpose-built databases to unlock the new insights contained in this data which is often persisted in multiple platforms and environments located in distributed locations. Thus, it is not surprising to see IT running mixed database workloads to support the business. Common examples include:
- Relational databases traditionally run core applications where the integrity of business data is a must. They are compliant with ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability), which is a standard set of properties for reliable database transactions. (Examples: Microsoft SQL, Oracle, SAP HANA, MySQL)
- NoSQL databases typically includes any database that does not use SQL as its primary data access language. Unlike relational databases, NoSQL databases do not conform to pre-defined schema allowing them to process larger amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data at speed. (Examples: MongoDB, Apache Cassandra)
- Document databases are NoSQL data stores that are designed to store documents with their meta-data. The document model works well with use cases such as catalogs, user profiles and content management systems where each document is unique and evolves over time. (Examples: MongoDB, Amazon DynamoDB, Google Cloud Firestore)
So, what does this mean for IT?
With data‑driven applications coming of age both in the consumer space and the business realm, IT needs a modern foundation addressing the advancements and new operating profiles for database platforms, bringing structured operational data together with unstructured data (including AI technologies such as machine learning and blockchain) which next-gen applications are built on. Specifically, IT needs a strategy to consolidate and run mixed database use cases with modern Infrastructure as-a-Service (IaaS) which:
- Provides the control and agility IT needs to scale as database use cases evolve and increase.
- Enables an agile, secure database strategy with data access regardless of location.
- Enhances developer productivity with structured, unstructured, machine, IoT data sets and database containers.
This is where Dell Technologies APEX solutions comes into focus
First, Dell Technologies APEX solutions provide efficient, intelligent systems that scale up and out with your database demands. Our IT offers are designed for ease of use, reliability and lifecycle management allowing valuable resources to focus on business innovation by freeing IT staff from repetitive tasks.
Additionally, Dell Technologies APEX enables an agile, secure data strategy, empowering business decisions based on operational data together with unstructured, machine and big data. We help bridge the edge-to-multi cloud data gap enabling database workloads to work with data regardless of location, secure data with cyber confidence by providing cyber‑resilient IT and a path to recovery from ransomware and destructive cyberattacks and streamlining data ingestion and access with unlimited retention, including access to both real‑time and historical events.
Lastly, our solutions help enhance developer productivity with data. For accelerating DevOps, APEX Data Storage Services with Dell EMC CSI Plugins simplifies the provisioning of persistent storage for container databases, empowering teams with the portability needed to build locally, deploy to the cloud and run anywhere. And for AI‑enabling infrastructure, we provide modern compute, GPUs, storage and network services to ensure high performance for in-memory database workloads working with ML, Blockchain etc.
Use cases
Below, I have highlighted several database use cases for tradition and purpose-built databases with Dell EMC Validated Designs.
Mission critical applications and relational databases
Historically, large application and databases running core business functions have been deployed on isolated infrastructure. In many cases, ensuring high performance for production systems has been a primary driver. Over time, siloed IT running production and non-production became a norm. Today, Dell Technologies APEX modern compute, storage and data protection platforms make it feasible to consolidate and run mixed OLTP, OLAP and analytic environments on shared infrastructure as a service for reduced TCO and simplified IT management and operations. Read more: Oracle RAC Reference Architecture and Microsoft SQL Server Reference Architecture
Cloud native applications and databases
One of the most powerful tools in cloud native architectures is containerization working with Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server or no-SQL databases such a Mongo DB and Cassandra. While container technology enables development teams to quickly provision isolated databases, you need to maintain persisted data somewhere on the network providing the performance, scale, and availability for applications dependent on “stateful” database containers. Read more about provisioning and securing the cloud native databases in cloud native infrastructure with Dell EMC: Cloud Native Databases Technical White Paper
Data virtualization: databases and big data
Enterprises are making significant investments to develop data management strategies for data warehouses, data marts, data lakes, and so on. The ability to quickly integrate new data sources located in dispersed is a critical dependency for enabling business functions to move from historical reporting to predictive, actionable insights. Dell Technologies has invested in validated designs to demonstrate how data virtualization can be an efficient and seamless experience for application developer use cases with Oracle and Microsoft SQL. Read more: Oracle Big Data White Paper and Microsoft Big Data SQL White Paper
No-SQL databases
Increasingly new applications are running on no-SQL databases that are designed to be flexible and scale for large datasets consisting of unstructured data like sensor data, media post and machine data. An important ingredient is flexible highly performant scale-out storage and compute platforms with secure data protection, high availability and inline data reduction reducing storage consumption and costs. Read more: Dell EMC Solution Guide for Mongo DB
In summary, the APEX portfolio delivers cloud services for a range of database requirements, enabling organizations to simplify transformation and adapt to evolving conditions while staying in control of their data. These offerings reduce the time and complexity of acquiring, managing, maintaining and servicing IT infrastructure. Organizations can scale IT as needed to launch new applications, kickstart new projects and address the changing needs of their organizations with APEX services managed by Dell Technologies and accessed through a single console.
Here’s a quick look at the offerings in the APEX portfolio:
- APEX Cloud Services provide a consistent cloud experience across public cloud, private cloud and edge environments. These services are ideal for compute-intensive AI projects.
- APEX Data Storage Services deliver a simplified storage as-a-service experience with scalable and elastic storage resources built on industry-leading technologies.
- APEX Custom Solutions offer flexible payment and IT management services for the industry’s broadest infrastructure portfolio.
To learn more
Ready to power and accelerate your move to running mixed database workloads on modern infrastructure as a service solutions? Get to the APEX with Dell Technologies.
